🔬 Let’s break some systems together! Our potential research directions are listed on this page for your reference and you can reach out to us to learn more. Also, feel free to BYOI (Bring Your Own Ideas) - your input is highly valued!
General direction
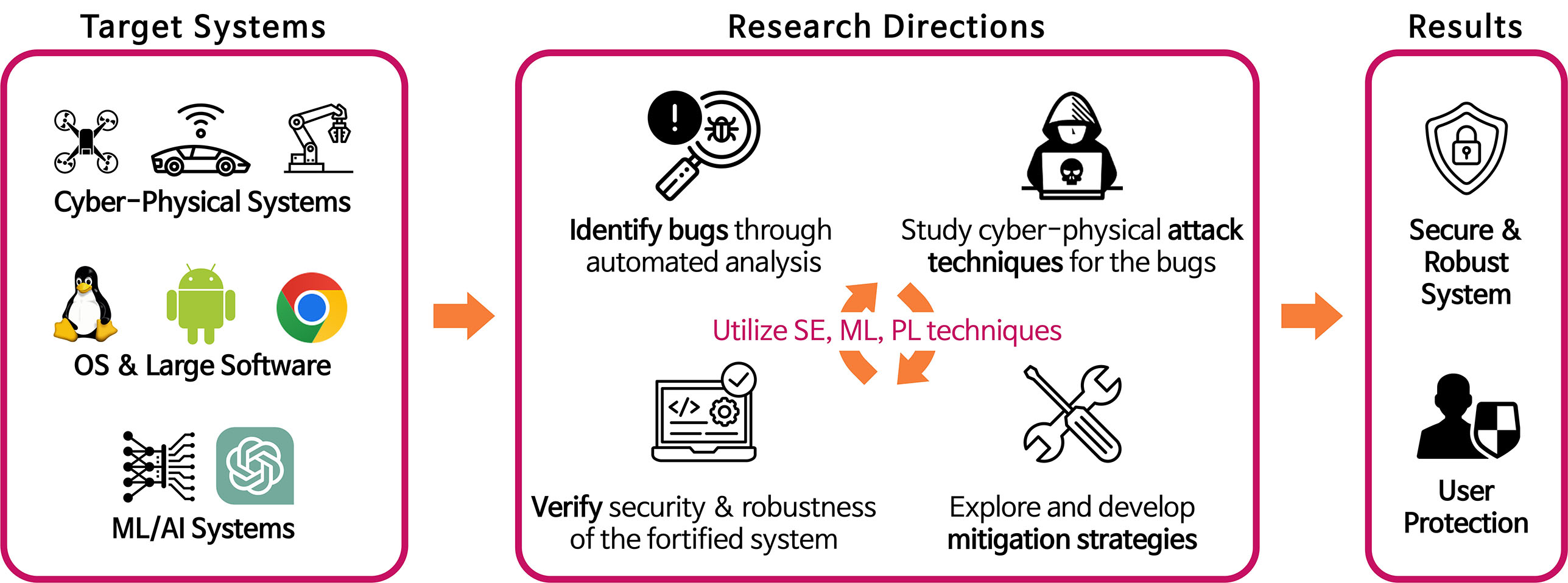
Target: Cyber-Physical Systems (CPS)
- Lead: Prof. Seulbae Kim
- Subject systems: robots, drones, autonomous vehicles, satellites, …
1. Verification of logic/algorithm implementation
- Key question: Are there any discrepancies between the intended logic/algorithm and the actual software implementation?
- Reference: RoboFuzz, DriveFuzz
2. Tailoring automated software testing techniques for distributed CPS codebases
- Key question: Can we tailor existing testing techniques/metrics to CPS codebases that are designed as distributed systems?
3. Policy and testing methodologies for live/production systems
- Key question: How to guarantee safety of production systems during tests?
4. Analysis/discovery of physical attack vectors
- Key question: Can we systematically attack the software (or the entire cyber-physical system) through physical attacks?
- Reference: Acoustic attack
5. Creative attacks on sensor and perception layers
- Key question: How can we (silently) fool the eyes and brain of a cyber-physical system to (maliciously) affect its behavior?
- Reference: Frustum attack
6. Resource-constrained testing
- Key question: Many CPS have limited computing power and memory. Can we quickly reveal issues associated when these resources are scarce?
7. Cyber-physical security by design
- Key question: Can we carefully design the components of CPS to guarantee security? (e.g., by having secure channel between the hardware and software)
8. Exploring (the imperfectness of) physics simulators
- Key question: Three-dimensional physics simulators are widely used for robotic development and testing. Are there any potential caveats caused by the flaws of the simulators?
Target: Operating Systems and Large Software Systems
- Lead: Prof. Seulbae Kim
- Subject systems: Linux/Windows Kernel, web browsers, …
1. Automatically identifying non-memory issues (e.g., performance deradation)
- Key question: How to design test oracles and testing methodologies for the issues that do not readily manifest (e.g., performance degradation)?
2. Efficiently testing emulated systems
- Key question: Emulation comes at a cost of (terrible) performance. Can we somehow skip the slow part for testing purposes?
3. Improving fuzzing methodologies
- Keywords: Directed fuzzing, AI-assisted fuzzing, in-memory fuzzing, …
4. Automated Game testing
Target: AI/ML Security
- Lead: Prof. Sangdon Park
- Subject systems: Generative AI, Robot AI
1. Find vulnerabilites of Generative AI!
- Can we find prompts of Large Language Models (LLMs) to generate sensitive information?
- You can suggest the rest to me!
2. Secure Generative AI via ML!
- Can we unlearn sensitive information from LLMs?
- You can suggest the rest to me!
3. Find vulnerabilites of Robot AI!
- Can we find adverarial attacks to drive robots to unsafe states?
- You can suggest the rest to me!
4. Secure Robot AI via ML!
- Can we learn individual AI for securing Robot AI?
- You can suggest the rest to me!
Target: Code
- Lead: Prof. Sangdon Park
- Subject systems: many program code
1. Find vulnerabilites of code using LLMs!
- Can we learn LLMs to find vulnerability of code and patch the code?
- You can suggest the rest to me!